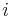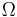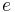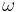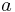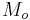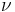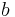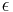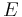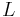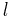Medium Earth orbit
Medium Earth orbit (MEO), sometimes called intermediate circular orbit (ICO), is the region of space around the Earth above low Earth orbit (altitude of 2,000 kilometres (1,243 mi)) and below geostationary orbit (altitude of 35,786 kilometres (22,236 mi)).[2]
The most common use for satellites in this region is for navigation, such as the GPS (with an altitude of 20,200 kilometres (12,552 mi)), Glonass (with an altitude of 19,100 kilometres (11,868 mi)) and Galileo (with an altitude of 23,222 kilometres (14,429 mi)) constellations. Communications satellites that cover the North and South Pole are also put in MEO.[3]
The orbital periods of MEO satellites range from about 2 to 24 hours.[4] Telstar, one of the first and most famous experimental satellites, orbits in MEO.[5]
The orbit has a moderate number of satellites.
See also
- List of orbits
- Low Earth orbit (LEO)
- High Earth orbit
- Highly elliptical orbit (HEO)
- Geostationary Earth orbit (GEO)
- Geosynchronous orbit (GSO)
Notes
- ^ Orbital periods and speeds are calculated using the relations 4π²R³ = T²GM and V²R = GM, where R = radius of orbit in metres, T = orbital period in seconds, V = orbital speed in m/s, G = gravitational constant ≈ 6.673×10−11 Nm²/kg², M = mass of Earth ≈ 5.98×1024 kg.
- ^ MEO 【Intermediate Circular Orbit】 (Medium Earth Orbit) - e-Words - A Glossary of Computers and Internet
- ^ Satellite Basics: Solution Benefits
- ^ What is MEO satellite? - a definition from Whatis.com - see also: MEO, medium earth orbit satellite
- ^ Medium Earth Orbit